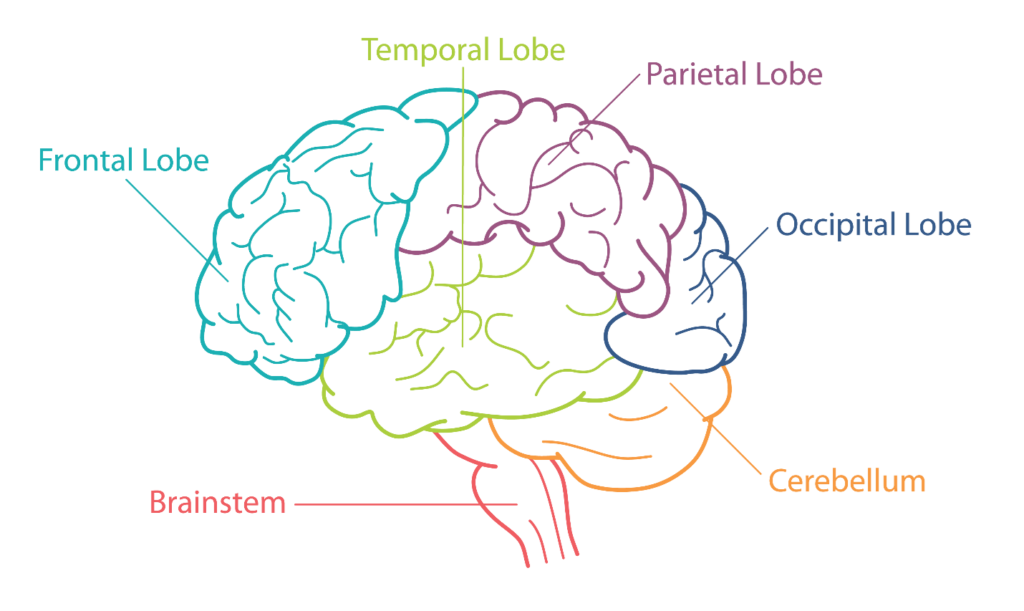
It’s Brain Stem, Its location means it’s where your brain and spinal cord connect, making it a key conduit for nerve signals to and from your body.
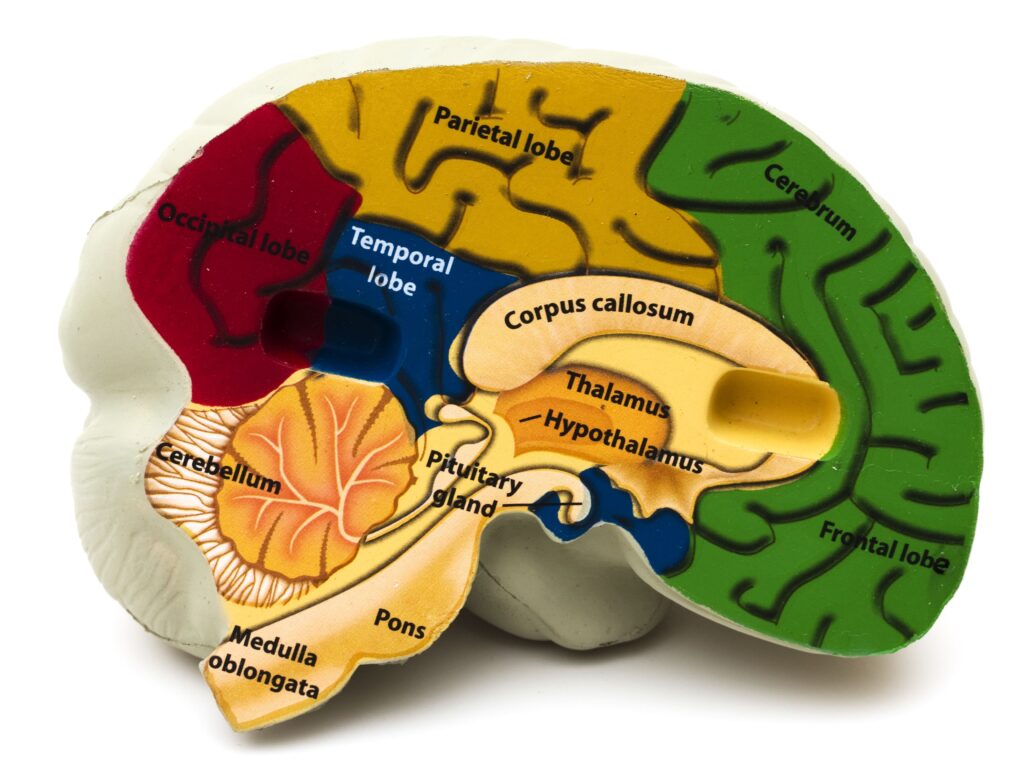
Brain Stem also contains 3 main parts i.e. the Medulla Oblongata, the Pons & the Mid Brain. We will discuss only about the Medulla Oblongata in this blog for now.
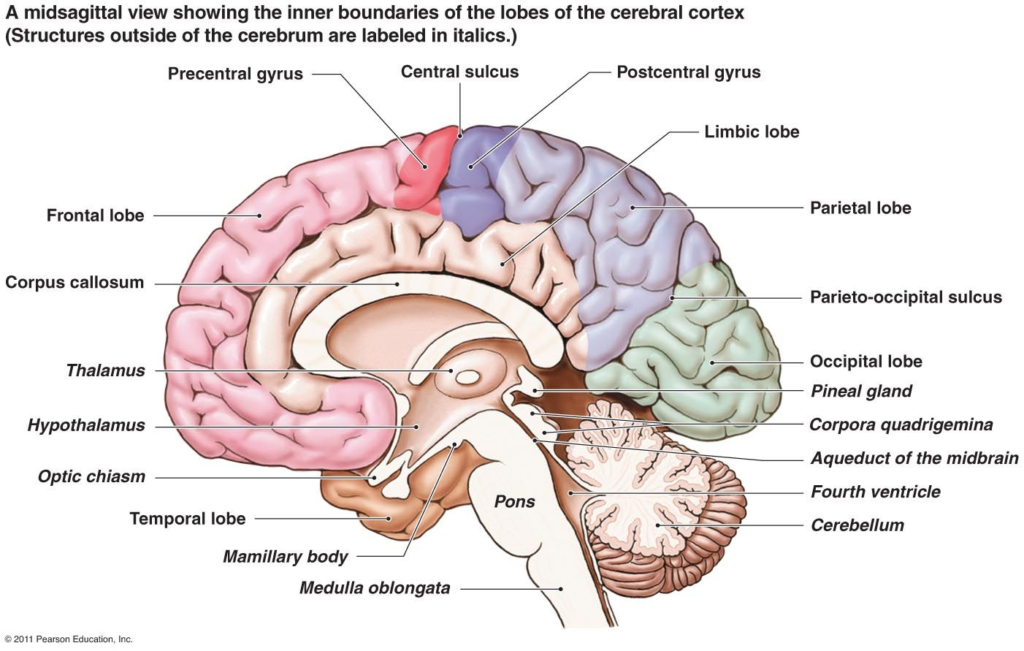
- Medulla Oblongata is the most bottom part of your brain stem.
- Your medulla oblongata plays a vital role in regulating those involuntary processes. Without this vital section of your brain, your body and brain wouldn’t be able to communicate with each other.
- It also helps control vital processes like your heartbeat, breathing and blood pressure.
- It is the direct upwards continuation of the spinal cord.
- It extends from the foramen magnum to the lower border of the pons.
- Vertically in the anterior part of posterior cranial fossa between the clivus in front & vallecula of cerebellum behind.
- Truncated cone- bulb like.
- 3 cm in length & 2 cm in breadth.
- Contains vital centers:
- Cardiac Centre: The cardiac Centre is a part of the human brain within medulla oblongata which regulates heart rate through the nervous system & endocrine system. Hence, it is one of the vital Centre of the medulla oblongata. In various conditions like exercise and major trauma, the cardiac Centre is responsible for altering heart rate.
- Vasomotor Centre: The vasomotor Centre has a vasoconstrictor area that sends sympathetic impulses reach to arterioles, arteries and virtually all organs through spinal cord. It is located in the reticular substance of medulla & lower third of pons bilaterally. It is responsible for regulation of cardiac electrical activity, myocardial performance and peripheral vascular tone.
- Respiratory Centre:
The medulla oblongata also known as the primary respiratory control Centre because it consists the respiratory Centre. It plays an important function i.e. send signals to the muscles that control respiration to cause rhythmic breathing (normal like quiet breathing at rest or during sleep) is regulated by the respiratory Centre in the medulla oblongata of our brainstem.
- Attachment to last four cranial nerves.
- The lower part of the medulla like the spinal cord contains the central canal.
- Upper part of the medulla this canal widens & moves dorsally to form the lower part of the fourth ventricle.
- Divided into lower part closed & an upper open part.
- It have rootlets of IX to XII cranial nerves.
External features of Medulla Oblongata:-
- The medulla is divided into the right & left symmetrical halves by anterior median fissure & posterior median sulcus.
- The anterior median fissure is continuous with the corresponding on the spinal cord & above it ends into a small triangular depression called Foramen Caecum at the lower border of pons.
- It is interrupted in it’s lower part by the bundle of the fibres crossing obliquely from one side to other- Decussation of pyramids.
- The posterior median sulcus continues below with the corresponding sulcus of the spinal cord.
- Each half of medulla is marked by two sulcus- anterolateral & posterolateral.
- Anterolateral sulcus extends along the lateral border of the pyramid & along it emerges the rootlets of the hypoglossal nerve (XII).
- The posterolateral sulcus lies between the olive & the inferior cerebellar peduncle & along it emerges the rootlets of glossopharyngeal (IX), vagus (X) & accessory (XI) cranial nerves.
Ventral aspect of Medulla:
- Pyramids: These are two elongated elevation one on either side of the anterior median fissure & are produced by the corticospinal fibres.
- Olives: These are oval elevation posterolateral to the pyramids & are produced by underlying mass of grey matter- inferior olivary nucleus.
Dorsal aspect of Medulla:
- Lower closed part
On either side of posterior median sulcus presents three longitudinal elevations.
From medial to lateral these are-
- Fasciculus Gracilis: The gracile nucleus carries information from the lower torso and the lower limbs.
- Fasciculus Cuneatus: The cuneate nucleus carries information from the upper body and the upper limbs.
- Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle: Each cerebellar inferior peduncle connects the spinal cord and medulla oblongata with the cerebellum.
- Upper open part
The open part forms the lower part of the floor of the fourth ventricle.
Blood supply of Medulla Oblongata:
- Two vertebral arteries: Paired vertebral arteries provide blood supply for the upper part of the spinal cord, brainstem, cerebellum, and posterior part of the brain.
- Anterior & posterior spinal arteries: The vertebral arteries are the main source of blood to the spinal cord. However, the following arteries branch from the vertebral arteries to directly supply the spinal cord itself: one anterior spinal artery. two posterior spinal arteries.
- Anterior & posterior inferior cerebellar arteries: The anterior inferior cerebellar artery supplies the middle cerebellar peduncle, lower lateral pons, anteroinferior surface of the cerebellum, flocculus and the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricle. The posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) is the largest branch of the vertebral artery. It is one of the three main arteries that supply blood to the cerebellum, a part of the brain.
- Basilar artery: The basilar artery is the main artery that supplies blood to the back portion of your brain. It carries oxygenated blood to your brainstem, cerebellum and occipital lobes.
Hope you guys understood this very well. If you want proper notes on this topic or on neuroanatomy then contact us.
